Ozone could turn cities into no-go zones

Hazardous levels
Unlike heavy air pollution in winter, mainly caused by PM2.5 and PM10 which bring thick haze and reduce visibility, ground-level ozone pollution occurs when the skies are blue and the sun's rays are strong. That means few people notice the ozone concentration rising to hazardous levels.
The rise in ground-level ozone has become a big issue for governments fighting to improve the air quality in their cities and regions.
A growing number of cities have seen rises in ground-level ozone. In 2015, of the 74 major cities in which air pollution was monitored regularly, only 62.2 percent recorded ozone levels below the national standard of 160 micrograms per cubic meter over an average of eight hours.
The figure surprised observers because many cities nationwide had previously witnessed reductions in ozone levels. In 2013, 76 percent of monitored cities reported levels below the national standard, while in 2014 the figure was 67.6 percent, according to data from the Ministry of Environmental Protection.
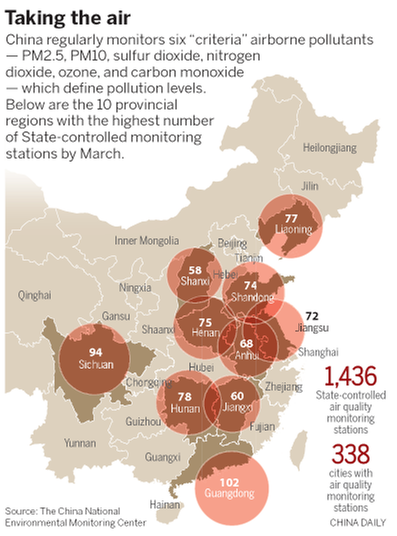
Scientists use six "criteria" airborne contaminants to define pollution levels: PM2.5; PM10; sulfur dioxide; nitrogen dioxide; ozone; and carbon monoxide.
Generally, people regard PM2.5 as the prime constituent of China's airborne pollution, and it has been targeted as the biggest enemy of the national campaign against air pollution.
Now, ground-level ozone has replaced PM2.5 as the biggest airborne pollutant in China's southern regions.
For example, in South China's Pearl River Delta, 56.5 percent of polluted days in 2015 were the result of excessive levels of ozone, a rise from 31.9 percent in 2013, according to the ministry's data.
Even the smog-prone northern regions, including the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei cluster, have seen rises in the number of summer days with excessive ozone.
In 2015, more than 17 percent of polluted days in the cluster were the result of excessive ozone, a rise from 7.6 percent in 2013, the ministry's data said.
"In June last year, ground-level ozone pollution saw Beijing listed in the top 10 cities (among the 74 monitored cities) for air pollution," Zhang Dawei, director of the Beijing Environmental Monitoring Center, said.
Lyu, from the meteorological administration, noted that China's vast northern and central regions, including the provinces of Hebei, Henan and Gansu, reported rises in ozone levels during the first half of last year.
Control measures
"We have noticed the climbing level of ozone in many regions and have taken strict control measures, but it will take time to reduce it effectively," said Zhao Yingmin, vice-minister of environmental protection, at a February media briefing in Beijing.
Ground-level ozone only forms when its precursors-mainly nitrogen oxides and volatile organic compounds that are easily transformed into gases or vapors-react in the presence of strong sunlight, Zhao said, citing the ministry's research data.
He pointed out that while many countries have solved the problem of PM2.5, they, like China, are also struggling to contain rising concentrations of ground-level ozone.
The ministry has issued regulations to reduce emissions of precursors by levying extra charges on 14 industries, such as petroleum-refining, that discharge volatile organic compounds in pilot regions such as Beijing.
Last year, the State Council, China's cabinet, ordered governments at all levels to target nitrogen oxides, one of the main precursors, and ensure that by 2020 the level is 15 percent lower than in 2015. The move has already resulted in a reduction in emissions, according to Zhao.
Ministry data show that during the period of the 12th Five-Year Plan (2011-15), emissions of nitrogen oxides fell by 18.6 percent. The ministry has also issued a regulation that will see emissions of volatile organic compounds in industrial centers reduced by 15 percent by 2020, Zhao said.
Complex mechanism
However, it will take more than just emissions reductions to control the rise of ozone.
"The major challenge for the controls is the complicated chemical mechanism by which ozone is formed. Also, it's difficult to control emissions of dangerous compounds because many companies are sited in isolated areas, which makes it hard to monitor their activities," Zhao said.
He added that effective control of ozone pollution lies in thorough research into the levels of nitrogen oxides and volatile organic compounds present during the process of ozone formation. "The conditions (for forming ozone) are different across the country because different regions have different economic and industrial structures and pollution levels, so they need targeted measures," he said.
The existing controls on emissions of nitrogen oxides and volatile organic compounds are not as stringent as required, he said.
Lyu, the environmental engineer with the meteorological administration, suggested that more research should be conducted and data collection expanded to provide forecasts for ozone pollution.
She said that in addition to the growing level of emissions from heavy industry and vehicle exhausts, the problem may be closely connected with global warming and rising terrestrial radiation: "In truth, the root of the problem lies in excessive emissions caused by human activity."
- Mainland denounces Taiwan-US trade deal as 'sellout pact'
- Beijing becomes China's second 5-trillion-yuan economy in 2025
- Strengthening trade bonds benefits people across Taiwan Strait: spokesperson
- Chinese researchers develop eye surgery robot
- High-speed train staff members in Beijing busy preparing for Spring Festival travel rush
- Mainland says DPP's so-called trade deal with US sells out Taiwan's interests





































