China builds three-satellite constellation in Earth-moon space

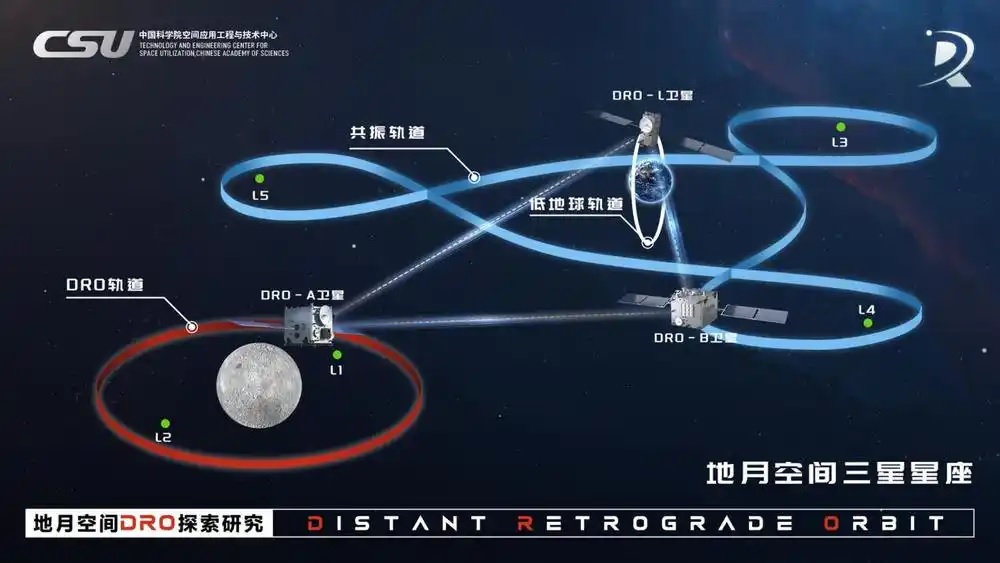
BEIJING -- China has successfully established the world's first three-satellite constellation based on the Distant Retrograde Orbit in the Earth-moon region of space, laying a foundation for the exploration and utilization of space, and for future crewed deep-space exploration.
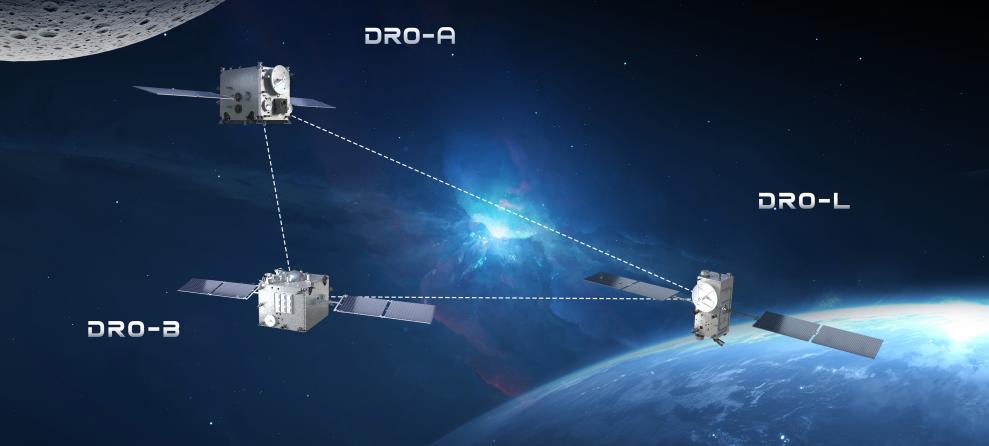
DRO-A and DRO-B, two satellites developed by the Chinese Academy of Sciences and deployed in the DRO, have established inter-satellite measurement and communication links with DRO-L, a previously launched near-Earth orbit satellite. The achievement was disclosed at a symposium on Earth-moon space DRO exploration in Beijing on Tuesday.
DRO is a unique type of orbit, and the Earth-moon space refers to the region extending outward from near-Earth and near-lunar orbits, reaching a distance of up to 2 million kilometers from Earth. In the Earth-moon space, DRO is characterized by a prograde motion around Earth and a retrograde motion around the moon, said Wang Wenbin, a researcher at the CAS' Technology and Engineering Center for Space Utilization.
Since DRO provides a highly stable orbit where spacecraft require little fuel to enter and stay, it serves as natural space hub connecting Earth, the moon and deep space, offering support for space science exploration, the deployment of space infrastructure, and crewed deep-space missions, Wang said.
On Feb 3, 2024, the experimental DRO-L satellite was sent into a sun-synchronous orbit and began conducting experiments as planned. The DRO-A/B dual-satellite combination was launched from the Xichang Satellite Launch Center in southwest China's Sichuan Province on March 13, 2024, but failed to enter its intended orbit due to an anomaly in the upper stage of the carrier rocket.
Facing this challenge, the satellite team performed a "life-or-death" rescue operation under extreme conditions, promptly executing multiple emergency orbit maneuvers to correct the trajectory of the two satellites.

After a journey of 8.5 million kilometers, the DRO-A/B dual-satellite combination ultimately reached its designated orbit, according to Zhang Hao, a researcher at CSU who participated in the rescue operation.
On Aug 28, 2024, the two satellites were successfully separated. Later, both DRO-A and DRO-B established K-band microwave inter-satellite measurement and communication links with DRO-L, testing the networking mode of the three-satellite constellation, Zhang said.
Currently, the DRO-A satellite stays in DRO, while the DRO-B satellite operates in Earth-moon space maneuver orbits, according to CSU.
The satellites ultimately succeeded in entering their designated orbit, demonstrating China's breakthroughs in deep-space fault recovery and autonomous navigation technologies. This achievement highlighted the satellite team's flexibility and adaptability in complex missions, and paved the way for low-cost deep-space exploration, said Zhang Jun, a senior engineer at the CAS' Innovation Academy for Microsatellites.
Wang Qiang, deputy director of CSU, said that following the successful networking of the constellation, a series of cutting-edge scientific and technological experiments have been conducted, driving research on the Earth-moon space.
In 2017, the CSU research team initiated studies on DRO in the Earth-moon space and tackled key technological challenges, proposing the concept of a DRO-based spaceport. In February 2022, CAS launched a plan to build the DRO-based three-satellite constellation in the Earth-moon space.
The project achieved the world's first spacecraft entry into DRO with low energy consumption. Through innovative design, the team completed a lunar transfer and DRO entry by using just one-fifth of the fuel usually required. This breakthrough has significantly reduced the costs of entry into the Earth-moon space, paving the way for the large-scale exploration of the Earth-moon space, Zhang Jun said.
Additionally, the project validated the K-band microwave measurement and communication links between the satellites and the ground at a distance of 1.17 million kilometers, achieving a key-technology breakthrough for large-scale constellation construction in the Earth-moon space, Zhang said.
Addressing challenges such as insufficient ground-based tracking and control precision, as well as the high costs and low efficiency of lunar and deep-space exploration missions, the research team pioneered a satellite-to-satellite, space-based orbit determination system.
By using three hours of in-orbit inter-satellite measurement data, the team achieved an orbit determination precision level that would typically require two days of ground-based tracking. This advancement has significantly reduced operational costs and improved the efficiency of spacecraft in the Earth-moon space, Zhang added.
In the future, the research team will continue investigating the complex and diverse orbits in the Earth-moon space, and study the laws of the lunar space environment. Leveraging the long-term stability of DRO, scientists will carry out fundamental scientific research in such fields as quantum mechanics and atomic physics, according to Wang.
- Pact to boost China's gold market
- Annual lantern festival opens in Shanghai
- Work teams dispatched after earthquake hits Diebu county in Gansu
- Zhangjiajie National Forest Park transforms into a winter paradise
- Thousands enjoy freshly cooked laba porridge in Sichuan
- Short videos highlight the beauty of Hebei





































