Is Shenzhen model sustainable or replicable?


Forty-five years ago, Bao'an county was an underdeveloped town. Perched on the southern edge of China and rubbing shoulders with the Hong Kong, it was mostly farmland and fishing villages. But in 1979, it was named Shenzhen and designated as a city. A year later, it became one of China's earliest special economic zones. The rest, as they say, is economic history.
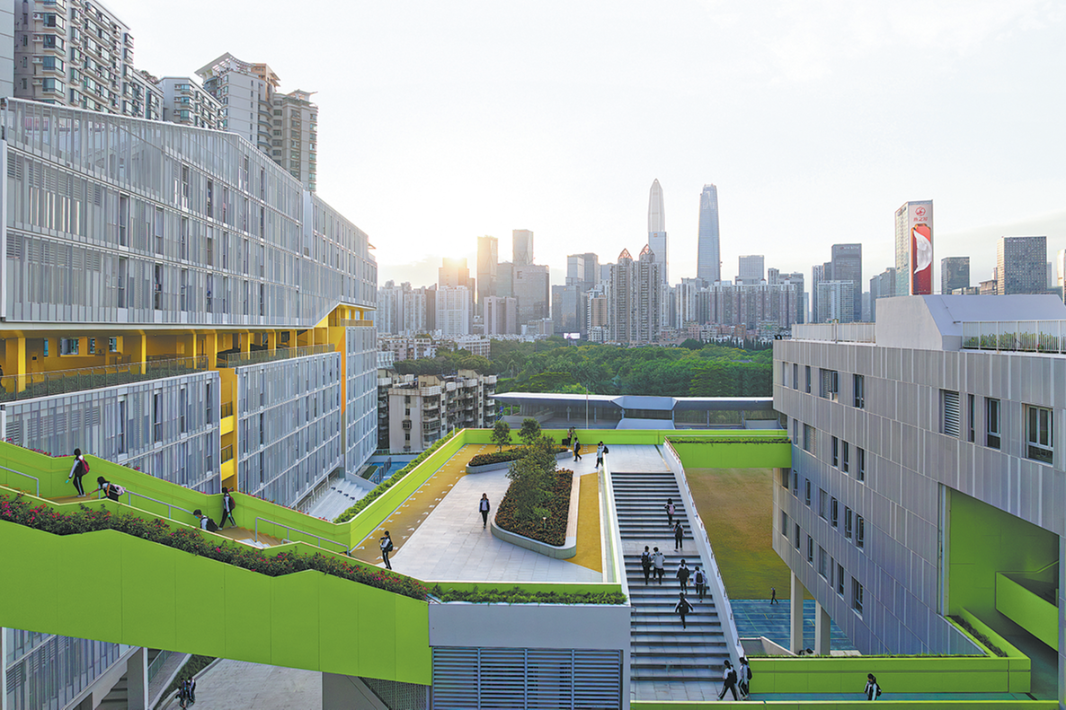
Fast forward to 2024. Today, Shenzhen is a very different place: a metropolis of glass towers, a magnet for start-ups, a hub for high-tech giants such as Huawei, BYD, DJI and ZTE. Its GDP now exceeds that of Hong Kong by 27 percent — a remarkable reversal of fortunes, considering its GDP once was just 0.62 percent of Hong Kong's economy.
This transformation raises a question echoed far beyond China's borders: Is Shenzhen's model of industrialization sustainable? And, more provocatively, can it be copied?
To answer that, we must go back to where it all began.
Shenzhen didn't start with shiny tech parks or unicorns. It started with the basics: labor-intensive manufacturing, known locally as the "three-plus-one" trade mix — custom manufacturing using supplied materials, designs, or samples, alongside compensatory trade. It was not glamorous. Nor was it high-margin. But it worked.
In a country with abundant workforce but short on capital, the model allowed Shenzhen to tap into global supply chains and develop economic muscles. Crucially, it also attracted entrepreneurs, investments, and people hungry for opportunity. In China's modern industrial awakening, Shenzhen was its classroom.
A mighty tree grows from a tiny seed. Shenzhen's story reminds us that the height of your starting point matters less than whether you've chosen a starting point that pays.
But integrating into global value chains was only the first step. What transformed Shenzhen from a low-cost workshop into a global tech powerhouse was its steady commitment to market-based reforms and rule-based institutions.
For 45 years, Shenzhen empowered its enterprises, not by shielding them from competition, but by exposing them to it. Markets weren't seen as a threat to policy, but as a vehicle for reform. Many of the early assembly-line enterprises moved up the ladder: from original equipment manufacturer to research and development, from anonymous factories to global brands.
Electronics manufacturing, because of Shenzhen's modularity and ease of relocation, clustered quickly in the city. This gave rise to an ecosystem that nurtured giant enterprises such as Huawei and ZTE. Other firms, like BYD and DJI, pivoted their core technologies — batteries, sensors, control systems — into sectors as diverse as electric vehicles (EVs), medical devices and drones.
It was a kind of industrial evolution by natural selection, but with a twist. The government established the initial rules of the game, but the market decided the winners.
Markets, however, can stall. And when they do, governments must act, not as dominating entities, but as guides. Shenzhen never mistook momentum for inevitability. In the 1990s, when it seemed the "three-plus-one" model had run its course, the city pivoted to cultivating private tech firms, building R&D parks, and promoting innovation. In the 2000s, it broadened that approach — offering incubators, improving intellectual property rights protection, and building regional innovation ecosystems.
By the 2010s, amid rising global tensions and tech restrictions by some economies, Shenzhen doubled down on resilience, strengthening the rule of law, fostering an open business environment, and promoting homegrown innovation. Innovation wasn't just about patents; it was about survival.
Consider this number. In 2024, Shenzhen produced nearly 2.94 million EVs — more than any other Chinese city. Not bad for a place that didn't make cars at all in the past.
The secret? Timing and trust in the market.
More than a decade ago, Shenzhen embraced the green transition early, backing pioneering EV companies such as BYD and Wuzhoulong. It electrified public transport fleets — buses, taxis — before electrification became fashionable. And it built entire industrial bases around EVs, not by picking winners, but by letting market signals drive scale.
By 2017, Shenzhen had become the world's first city to fully electrify its bus system. In 2024, EVs made up 76.9 percent of all new vehicle sales in the city. Shenzhen didn't just catch the EV wave — it helped create it.
There's another factor that rarely makes headlines but matters immensely: public participation.
Shenzhen's rise has never been free of criticism. From debates on whether the SEZ has lost its uniqueness to fears it is being left behind, the city has regularly engaged in introspection — including spirited public discussions involving senior officials. But these debates didn't paralyze action; instead, they sharpened it. Shenzhen has embraced feedback as fuel, not friction.
Each wave of public discourse ushered in a new wave of reform. The city's willingness to self-correct and welcome dissent may be the most replicable part of all.
So can the Shenzhen model be replicated?
Shenzhen's success is often seen as exceptional. In many ways, it is. But the underlying principles are surprisingly universal.
Start with what you have, however modest. Let the market do what it does best. Intervene strategically — when necessary — not to replace the market but to strengthen it. Promote innovation, protect competition and, above all, have faith in the initiative of the people.
These are not uniquely Chinese principles but common development lessons. For other developing countries seeking to industrialize in the 21st century, Shenzhen offers not just a model — but a mindset.
It's not about 3D-printing a tree. It's about planting your own seed, and letting it grow.
The author is vice-president of China Development Institute (Shenzhen).
The views don't necessarily represent those of China Daily.
If you have a specific expertise, or would like to share your thought about our stories, then send us your writings at opinion@chinadaily.com.cn, and comment@chinadaily.com.cn.