Breakthrough could deepen sea research
Chinese researchers develop electrohydraulic-driven soft robot

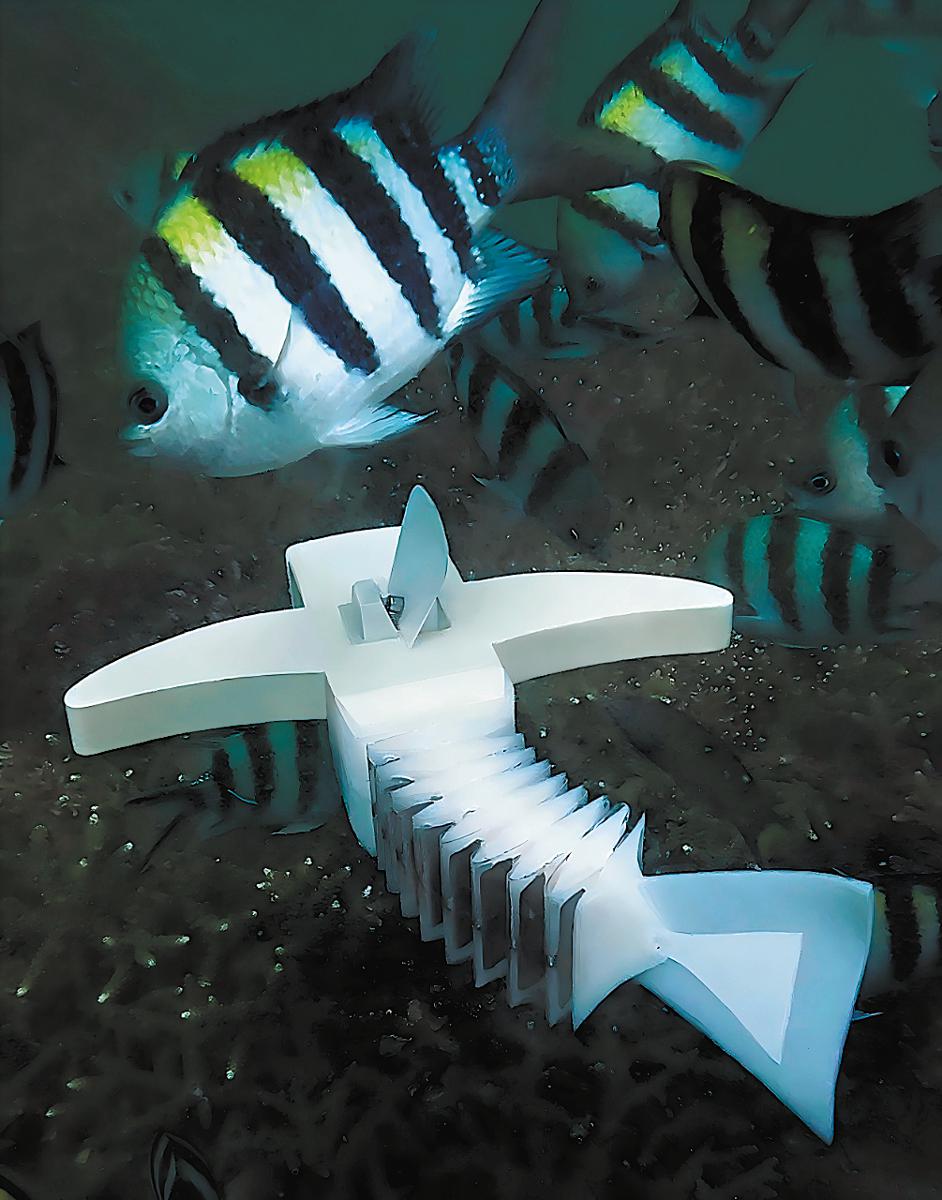
Patrolling in the dark seamount area at a depth of 4,070 meters, a robot fish about 32 centimeters long, with a wingspan of approximately 18 cm and weighing only 670 grams, glides flexibly along with all the real fishes.
This latest generation of the deep-sea soft robot is a new breakthrough in deep-sea exploration technology achieved by the research team led by Professor Li Guorui at the College of Shipbuilding Engineering of Harbin Engineering University in Heilongjiang province.
Their latest research, titled "Plasticized electrohydraulic robot autopilots in the deep sea", was published in the journal Science Robotics. Conducted in collaboration with Zhejiang University and the China Ship Scientific Research Center, the research team has developed an electrohydraulic-driven soft robot which has been applied to deep-sea exploration.
As the largest unexplored frontier on the earth, the deep sea holds the key to understanding life origins, resource exploration and climate evolution.
However, scientists face significant challenges due to extreme conditions such as high pressure and low temperatures during their exploration. There is also another obstacle: balancing the high costs of exploration and equipment reliability with the protection of fragile deep-sea ecosystems, according to the research team.
In 2022, the research team drew inspiration from the classical physical phenomenon of electrohydrodynamics to initiate the development of the electrohydraulic-driven deep-sea soft robot.
They innovatively applied the classical physical principle to design flexible equipment suitable for extreme deep-sea conditions.
By using an electrostatic field to control the orderly flow of dielectric fluid, researchers converted electric field forces into driving forces for flexible hydraulic units.
The designed electrohydraulic unit consists of a thin film shell, flexible electrodes and internal dielectric fluid, which flows directionally under Maxwell stress, precisely driving the flexible unit to produce controllable deformation.
The team systematically studied the large deformation effects of the flexible electrohydraulic unit under high pressure and low temperature, endowing the system with excellent deformation capabilities.
The dielectric fluid inside the driving unit can adaptively balance with the deep-sea water pressure, providing the system with full-depth pressure adaptability.
"The research team has been dedicated to exploring the expression and application expansion of the classical physical phenomenon in the mechanism of deep-sea electrohydraulic drive, which can provide a new approach for the design of driving systems for soft robots and intelligent equipment in extreme environments," said Li.
Without a pressure-resistant shell, the latest generation of the deep-sea soft robot can withstand the static water pressure at full ocean depth. The robot achieves coordinated drive of the electrohydraulic unit through its own miniaturized energy control system.
When electronic devices in the soft body generate high-voltage electrical signals, the flexible electrohydraulic unit will deform in a pattern similar to a fluid static skeleton under the stimulation of the voltage signal, enabling it to achieve various trajectory paths such as straight-line movement and turning in the deep-sea environment.
To further validate the reliability of the deep-sea soft robot in real-world deep-sea operations, the research team conducted a series of tests in various sea areas, including the Haima cold seep area and the deep-sea mountain area in the South China Sea.
On June 13, 2024, the robot was deployed at a depth of 3,176 meters in the South China Sea. Sea trial footage showed the robot successfully completed complex trajectory movements, near-bottom sensing, autonomous posture control, and return tasks in the challenging deep-sea flow environment.
On July 9, 2024, the robot conducted navigation tests at a depth of about 4,070 meters in a deep-sea mountain area, exploring the feasibility of coordinated operations between deep-sea submersibles and small deep-sea soft robots for large-area, low-disturbance deep-sea exploration.
Additionally, to further verify the ecological integration characteristics of the soft robot with the underwater environment, the team conducted in situ, close-range behavioral observations of the marine ecological environment and communities.
"After enduring multiple rigorous sea trials, the soft robot has demonstrated excellent mobility, reliable adaptability to extreme environments, and low-disturbance detection capabilities," said Shen Peng, a member of the team. "It holds promise for providing sustainable technological pathways and innovative methods for deep-sea ecological observation."
Currently, the team is focusing on interdisciplinary exploration in mechanics, information and manufacturing to develop miniaturized deep-sea soft robots with integrated driving, sensing, and communication capabilities, as well as swarm intelligence.
In the future, they aim to overcome key challenges related to material durability, system reliability and intelligence levels of flexible equipment in extreme environments, according to the team.
zhouhuiying@chinadaily.com.cn



































