Threat of antibiotic resistance
Excessive use of antibacterial drugs is making the medicines ineffective, which could kill more people than cancer by 2050
As the use of antibiotics at China's healthcare facilities comes under increasingly strict control, public health experts at home and abroad are turning their attention to agriculture and calling for enhanced management to prevent potential overuse in the sector.
Every year, 50 percent of the antibiotics employed in the world are used in China, with 52 percent of them used to treat animals bred for food, according to the latest report on international antibiotic use, led by Jim O'Neill, former chief economist at Goldman Sachs, who also was an adviser to David Cameron, the former British prime minister.
|
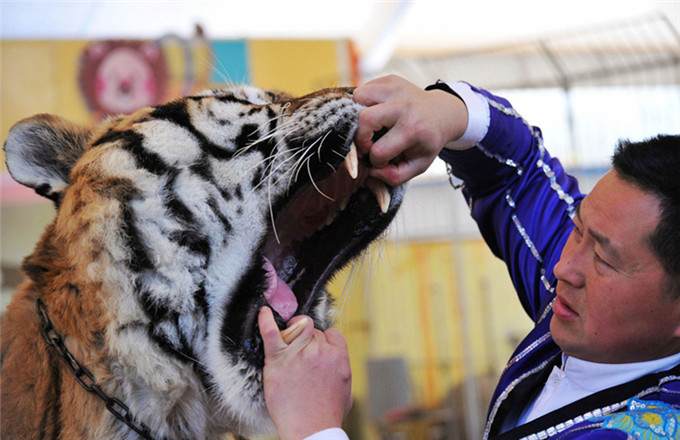
Regulations on the use of antibiotics in animal feed are not strictly enforced in China, and the country has no maximum residue limits for antibiotics detected in animal products such as meat and milk. Tan Kaixing / For China Daily |
The report, called the Global Review on AMR (antimicrobial resistance), warns that by 2050, antimicrobial resistance could be responsible for killing 10 million people across the world every year, the equivalent of one person every three seconds - higher than the annual global death toll from cancer.
It also estimates that by 2050, AMR could result in 1 million premature deaths every year in China. AMR occurs when microbes evolve to become increasingly, or fully, resistant to previously effective antibiotics.
"China could suffer an enormous loss of GDP because of that," O'Neill writes in an email exchange with China Daily.
He adds that the government recognizes the issue as one of crucial importance and has made efforts to curb excessive antibiotic use, particularly for medical purposes.
Statistics from the National Health and Family Planning Commission show that antibiotic use in China's hospitals has fallen by 40 percent since 2012, when the commission imposed measures - including stricter controls, prescription-only access and health education - to curb long-term excess use.
However, the report notes that the lack of stringent supervision in the agricultural sector must also be corrected.
Xiao Yonghong, a professor at the Institute of Clinical Pharmacology at Peking University and a member of the commission's rational drug use committee, echoed those concerns, saying that while the abuse of antibiotics has almost been eliminated at large hospitals in cities, a lack of surveillance data means it's difficult to assess the scale of the problem at grassroots clinics.
"Antibiotic abuse in animal farming is still widespread in China," Xiao says, adding that the country has no maximum residue limits for antibiotics detected in animal products, such as meat and milk.
"The antibiotic residue is not screened before animal products hit the market," Xiao says, pointing out that regulations on the correct use of antibiotics in animal feed are not enforced strictly enough.
Su Jiufu, a duck farmer in Weinan, in the northwestern province of Shaanxi, says he doesn't think there is a problem: "I often eat the meat and eggs of the ducks on my farm."
He generally sells his produce to grocery stores in the local township. "Storekeepers have never asked me about antibiotic use," he says.
As an experienced farmer, Su acknowledges that antibiotic use is relatively common at duck farms because the birds are prone to diseases.
The most commonly used antibiotics are Ciprofloxacin and Jinsaiwei, which are regularly added to the ducks' food, he says.
"That's not only for treatment, but prevention. Otherwise ducks can easily contract viral hepatitis, duck plague and fowl cholera, which spreads quickly, causing deaths and a loss of income for the farmers," he adds.
Zeng Xiaoxiang, who owns a chicken farm in Meizhou, Guangdong province, sells about 100,000 fowls a year. She says white-feathered breeds of chickens commonly seen on market stalls need to be given antibiotics almost every day to treat and prevent diseases such as bronchitis and enteritidis, a type of salmonella.
"The drugs, mainly antibiotics, such as penicillin and amoxycillin, and vaccines cost 150,000 yuan ($22,600; 20,240 euros) every year," she says. "The doses are usually increased during winter, when chickens are at greater risk of disease."
Excessive antibiotic use has already taken a toll. In 2011, researchers detected the MCR-1 resistance gene - which renders colistin, a last-resort antibiotics for multidrug-resistant bacteria, ineffective - in 5 percent of chicken and pork samples collected from markets around the country.
However, by the end of 2014, the proportion had risen to 25 percent. Late last year, a study led by Liu Yiyun, a professor at South China Agriculture University in Guangzhou, Guangdong, was published in the renowned UK medical journal Lancet Infectious Diseases. The study found that the MCR-1 resistance gene had been identified in a number of samples provided by hospital patients in the province.
"The gene can pass around among certain types of bacteria that exist in both animals and humans," says Huang Liuyu, director of the Institute for Disease Prevention and Control with the People's Liberation Army.
According to Huang, excessive antibiotic residue in animal products could be transmitted to humans via the consumption of meat, eggs and milk, increasing the possibility of increased resistance to antibiotics.
Also, the problem may "travel" and contaminate people in other parts of the world as a result of increasing international travel and interpersonal exchanges, he says.
Globally, antimicrobial drugs are becoming less effective and the world is not developing enough new antibiotics to replace those that are now almost redundant, according to the UK report.
O'Neill, the leader of the UK study, emphasizes the need for measures to tackle the problem. "It's a serious global challenge, and thus it needs a global solution," he says.
shanjuan@chinadaily.com.cn