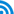Restructuring, Deleveraging and Keeping the Bottom Line: Measures Contributing to the Smooth Economic Performance
2015-08-18
—An analysis of economic situation in the first half of 2013 and prospects for the whole year
DRC Task Force on Analysis of Economic Performance
In the first half of 2013, the pace of China's economic growth slowed down, but remained within the expected range1. As China moves towards a moderate growth, previous growth modes remain but a new economic equilibrium has yet to emerge. Long-term structural discrepancies have become more apparent, as the economy experiences some uncertainty and instability.
Looking ahead to the second half of the year, international economic performance would continue to be stable, yet downward pressure on China's economy may increase. The Chinese economy must find a balance between restructuring, deleveraging, and smooth growth. The planned macroeconomic policies must protect the bottom line, promote stability, and place a top priority on controlling and mitigating regional and systemic risks, so as to maintain stability for economic growth and promote a smooth transition between different growth phases.
I. Downward Pressure on Economic Growth Intensified and Structural Discrepancies Emerged
In the first half of the year, downward pressure on the economy intensified. This was due to declining medium and long-term potential growth rates combined with insufficient short-term growth drivers, declining economic trends, and a relatively weak global economy. The arbitrage that exists within the financial system is creating a divergence between financial profits and real economic growth. In addition, the mismatch between workers' technical skills and the demand for highly skilled jobs, as well as other structural discrepancies continue to become more prominent.
1. A larger drop in PPI and delayed company restocking processes
PPI is usually a leading indicator for corporate inventory adjustments. After the third quarter of 2012, there was a short-term rebound in economic growth, largely driven by corporate restocking. Beginning in April this year, PPI dropped gradually, losing -2.7% in June. Meanwhile, the CRB (Reuters Commodity Research Bureau Index) fell and market expectations deteriorated once again. Inventories of finished industrial products grew by the relatively slow rate of 7%. Restocking effectively ceased in the chemicals, petroleum processing, ferrous metals, nonferrous metals, and other industries, and slowed down significantly in automobiles, special equipment manufacturing, general equipment manufacturing, among others. Many companies changed their previous inventory management models, whereby more and more companies used orders to determine production. The slowed restocking pace played a lesser role in driving short-term economic growth.

Figure 1 Changes of PPI(Producer Price Index)from June 2011 – June 2013
Source: State Statistics Bureau
2. Interest rate and exchange rate arbitrage continued to stimulate false RMB trades, causing abnormal import and export fluctuations
Because of China's capital account controls, offshore money is not easily able to enter into China. This has promoted the use of false trades to allow money to flow into China from such areas as Hong Kong, Macau, and Taiwan in China. False trades have increased significantly from the second half of last year, to the first half of 2013, resulting in abnormal import and export fluctuations. This was driven by factors such as: internal and external interest spreads, RMB appreciation, and temporary measures adopted by some local governments to encourage exports. False trading methods usually have involved trades originating from special customs supervision areas, with the trades concentrated primarily in precious metals, integrated circuits, or other easily transportable, high value products. However, after regulatory measures were strengthened in May, export growth dropped to 1% and -3% in May and June respectively, from 17.4% aggregate growth in the first four months of 2013. Excluding exports to Hong Kong, Macao, and Taiwan in china, Chinese export growth in the first half of the year dropped from 10.4% to 6%, and import growth dropped from 6.7% to 5.2%. If we simply look at normal trade, export growth in the first half of the year remained roughly unchanged, without significant improvement from the previous year.
3. Prominent capital efficiency issues and the disconnection between the virtual and the real economy
Presently, China has an adequate amount of liquidity. At the end of June, M2 and loan balances were RMB 105 and 68 trillion yuan respectively, or 200% and 130% of GDP last year. However, liquidity in the money market was limited because capital costs in the real economy were relatively high. A funding shortage appeared in June, which exposed problems that have arisen in the last few years, such as an unreasonable financial structure and an increasing amount of leverage. This has occurred because small and medium-sized banks can borrow from large banks at low rates, and circumvent regulations by lending to businesses at much higher rates. Furthermore, low-efficiency companies, industries experiencing overcapacity or cash flow problems, as well as highly-leveraged real estate ventures drained funding from the real economy and as a result, increased overall market interest rates directly affecting small and medium-sized enterprises. Meanwhile, the financial sector seemed prosperous and housing prices rose in spite of the global recession, but the majority of the real economy was in serious need of funding, thereby intensifying resource allocation distortions.
4. Local protections, a lack of effective exit mechanisms, and slow overcapacity adjustments
China's current overcapacity affects a wide range of industries, and there is a high degree of absolute overcapacity. In the context of the decline in medium and long-term growth, the conflict between downward economic growth pressure and overcapacity will deepen. Insufficient market demand often leads to low profits and even losses across an industry. An increased risk of widespread bankruptcies may lead to financial and fiscal risks. Meanwhile, fierce competition at the lower end of the value chain has prevented better performing companies from rising above the rest. In certain industries, backward production facilities could not be closed down properly and industry transformation and upgrading cannot be smoothly attained, which can undermine medium and long-term growth momentum to a significant extent. Accelerating capacity adjustment is the key to resuming stable profitability in the real economy. However, many industries with overcapacity are important to local governments for meeting GDP, tax revenues, and employment targets. These industries therefore often obtain support from local governments. In addition, due to the lack of effective exit mechanisms, a lot of inefficient or unprofitable "zombie" companies (insolvent companies) are forced to just barely remain in business, leading to slow production capacity adjustments.
5. Employment was generally stable, but structural problems cannot be ignored
In the context of the economic downturn performance, employment remained basically stable, according to current statistics. Demand for positions across the country slightly outpaced supply, and the vacancy-to-seeker ratio was slightly higher than 1. Recruitment difficulties still existed in some areas, and the demand gap for technical workers, skilled workers, and infrastructure engineers was especially large. At the same time, structural unemployment increased. The reasons for this are as follows: first, college graduates are having difficulty securing employment, as the graduate employment signing rate decreased significantly. Second, market demand continued to be sluggish, labor and capital costs were relatively high, and some SMEs began to reduce staff. Third, higher-end service industries such as catering, accommodation, exhibition, and entertainment all experienced a decline in demand, and part of this workforce has been met with frictional unemployment. The ratio of the demand for service industry positions to the demand for new positions declined by nearly 3 percentage points in the first quarter, compared to the fourth quarter last year. Wage growth in various industries and companies slowed, and changes in employment trends should be given adequate concern.
…
If you need the full text, please leave a message on the website.
1The average annual growth target set out in China's Twelfth Five-Year Plan is 7% and the annual target for 2013 is 7.5%.